Assisted reproductive techniques
- Home
- Uncategorized
- Assisted reproductive techniques
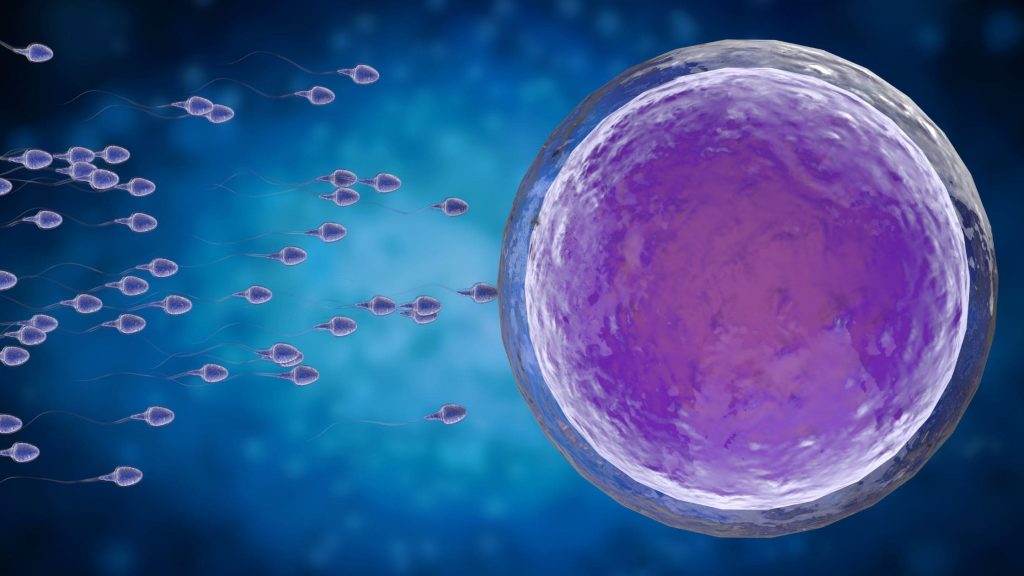
Assisted reproduction is the part of medicine that helps procreation when it does not come naturally. There are mainly two assisted reproduction techniques: artificial insemination and in vitro fertilization. The main difference between the two lies in the degree of assistance or help they provide in relation to the natural process of conceiving.
Artificial insemination (AI)
Artificial insemination is the least complex assisted reproduction technique. There is another procedure, programmed intercourse, which is simpler and much closer to the natural procedure. However, it is generally not considered as an assisted reproductive technique but as a gynecological aid to natural conception.
It is based simply on monitoring by ultrasound and blood tests the moment in which ovulation will occur to indicate to the couple when to have sex in search of pregnancy.
For its part, artificial insemination consists of introducing sperm through a cannula into the vaginal fundus at the time ovulation is going to occur. To better control ovulation, women should take low-dose hormonal medication. However, in some cases, it is done simply by following the natural cycle. For his part, the man must obtain a seminal sample by masturbation, which will be concentrated in the best quality sperm (a process known as “sperm capacitation”).
Said “improved” sample will be the one that will be deposited in the woman at the appropriate time.
It is said that artificial insemination is not a great help compared to the natural way because, once the semen is deposited in the vagina, the rest of the steps for fertilization and implantation have to pass naturally, that is, they are not controlled externally nor can you intervene on them. However, in many cases, this small intervention may be enough to achieve pregnancy.
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
In vitro fertilization or IVF is a much more complex process than artificial insemination. Foreign aid is much greater. In fact, the steps that have to occur naturally are simply two:
Creation of the embryo.
Implantation.
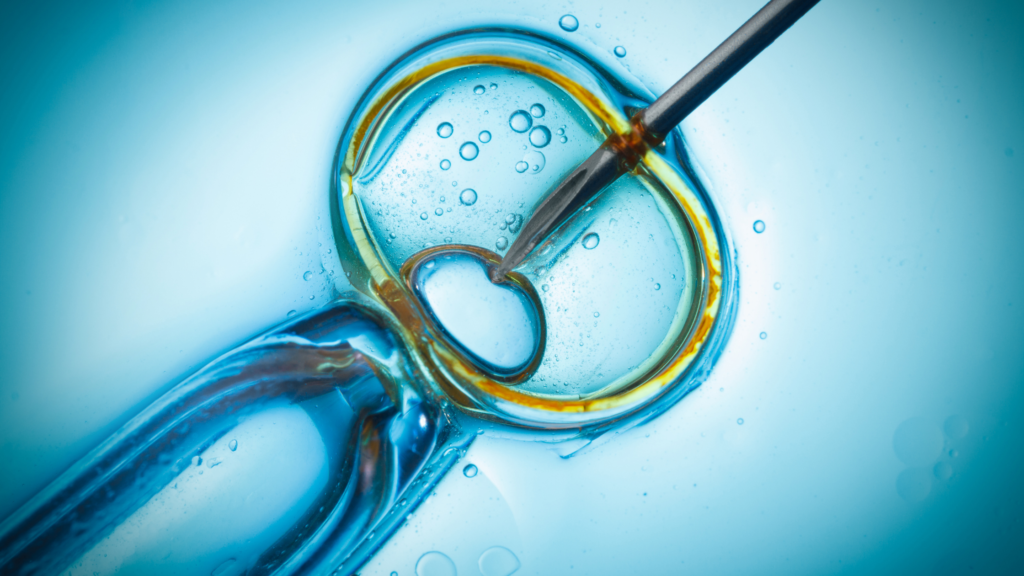
The IVF procedure basically consists of removing the eggs and sperm, joining them in the laboratory, obtaining the embryos and transferring them to the uterus while waiting for implantation to occur.
Eggs are removed from the ovary just before natural ovulation in a procedure known as “ovarian or follicular puncture.”
Sperm, meanwhile, are generally obtained by masturbation. In some cases they are taken directly from the testicle. With the gametes outside the body, the union of the same occurs in the laboratory, waiting for this union to be effective and give rise to embryos. This is one of the points that cannot be 100% controlled.
Once the embryos are obtained, the best one is chosen and transferred to the woman’s uterus, waiting for her to be able to connect with the uterus and implant in the uterine endometrium.
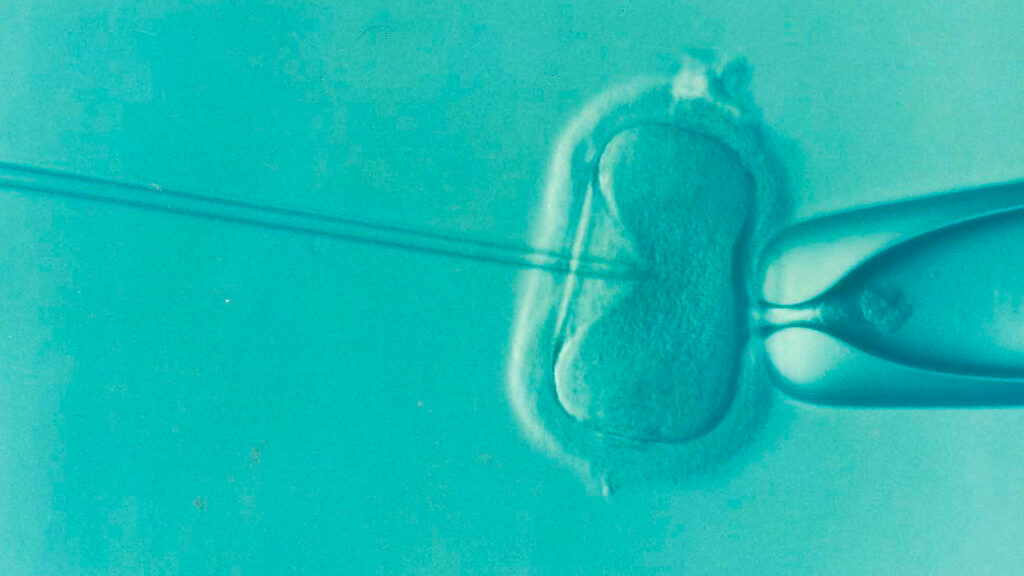
In the case of IVF, there are different laboratory procedures that act as a complement but are not usually considered as assisted reproductive techniques per se. The best example is ICSI, which refers to sperm microinjection of sperm.
It is a process to promote the union of ovum and sperm, that is, it is a way of carrying out in vitro fertilization itself. We will discuss this procedure in more detail in later articles.
Another example of a complementary technique to IVF is in PGD or preimplantation genetic diagnosis. This is a process that allows us to analyze the genetics of the embryo obtained in vitro before its transfer to the uterus to know whether or not it presents genetic alterations that could give rise to a sick child.
Today we have talked to you in a very summarized way about the two fundamental pillars of assisted reproduction. Later we will detail these and other laboratory procedures in a more specific way so that you can solve all your doubts.
You may also like
Azoospermia: qué es y cómo tratarla
Un hombre que tenga azoospermia (ausencia de espermatozoides tras eyaculación) no quiere decir que necesariamente no pueda tener hijos. Es …
Fecundación In Vitro: qué es y su proceso
La fecundación in vitro (FIV) es un técnica de reproducción asistida que tiene la finalidad de ayudar a las mujeres …
Inseminación Artificial: qué es y cómo se hace
Los procesos de reproducción asistida pueden parecer similares y a la vez diferentes entre sí. Todos ellos están pensados para …
MALE FERTILITY: What is it and how is it measured?
The reproductive system of men and women is very different. Just as women are born with all the eggs that …
Principales causas de infertilidad
Son muchas las posibles razones por las que el embarazo natural puede no llegar. Sin embargo, existen una serie de motivos que son más comunes y de los que hablaremos en profundidad en el artículo de hoy.
Técnicas de reproducción asistida
La reproducción asistida es la parte de la medicina que ayuda a la procreación cuando ésta no llega de forma natural. Existen principalmente dos técnicas de reproducción asistida: la inseminación artificial y la fecundación in vitro. La diferencia principal entre ambas radica en el grado de asistencia o ayuda que suponen en relación al proceso natural de concebir.